Abstract
In today’s world, every pet owner wants the best possible care for their furry friend. Advances in veterinary medicine have led to improved diagnostic tools, and one of the most significant game changers is CT scan. A CT scan (computed tomography) is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body. In veterinary medicine, CT scans are used to visualise internal structures, diagnose disease, and guide treatment plans
Introduction
CT Scan – the name is quite common in human medicine but nowadays it is also used as an advanced diagnostic tool in veterinary medicine. CT scan stands for computed tomography and is a type of radiological imaging study.
A combination of X-rays and computer technology is used to create 3-D images of the inside of the body. It shows detailed images of all parts of the body, including bones, muscles, fat, organs and blood vessels. In a standard X-ray, the energy beam is focused on the part of the body being examined. A panel on the back of the body detects changes as the electrical energy passes through the skin, bones, muscles and other tissues. Although a lot of information can be obtained from X-rays, not much detail is available about internal organs and other structures. This allows for more variations on the same body or structure and provides more detail. CT scans provide excellent clinicopathological correlation for a suspected illness.
Procedure
A CT scan involves the patient lying on a bed that slowly travels along the gantry as the x-ray tube spins around them, passing through their body to emit small beams of radiation. CT scanners use specialized digital x-ray detectors, which are placed immediately across from the x-ray source, in place of film. The detectors take up the x-rays as they exit the patient and send them to a computer.
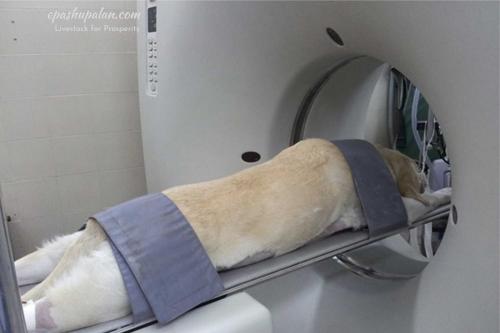
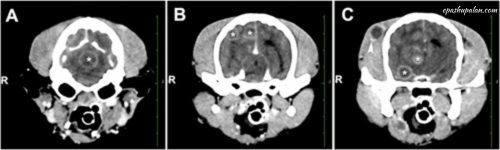
Benefits of CT scan in veterinary medicine
- Accurate diagnosis: CT scan provides high-resolution images, allowing veterinarians to diagnose conditions more accurately and earlier than ever before.
- Minimally invasive: CT scans are non-invasive, reducing the risk of complications and stress for your pet
- Quick and painless: scans are typically fast, taking only a few minutes, and your pet will remain comfortable throughout the process.
- Comprehensive Imaging: CT scans can image multiple body parts simultaneously, providing complete picture of your pet’s health.
- 5. Early disease detection: CT scans facilitate early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Applications of CT scan in veterinary medicine
- Cancer Diagnosis and Staging: CT scans help identify tumours, determine their size and location, and guide treatment plans.
- Neurological disorders: CT scans diagnose conditions like epilepsy and hydrocephalus.
- Orthopaedic Issues: CT scans evaluate bone fractures, joint diseases, and spinal conditions.
- Respiratory Problems: CT scans diagnose lung disease, such as chronic bronchitis and asthma.
- Cardiology: CT scans evaluate cardiac structures and functions, diagnosing conditions like heart failure and congenital defects.
- Ophthalmology: CT scans diagnose and monitor ocular disease such as proptosis, orbital fractures, and retinal detachment.
Disadvantages of CT Scan in Veterinary Medicine
- The biggest disadvantage of CT scan in pet animal is that it is a time consuming process due to the requirement of general anaesthesia.
- Requires good number of staff as Radiologist, Anaesthetist and Technician.
- CT scan always involves anaesthetic risk due to requirement of general anaesthesia.
- Expensive: A CT scan in general is an expensive procedure due to the cost of machine and all the requirements mentioned above.
- X-rays, which are used in CT scans, emit ionizing radiation. Living tissue may experience biological consequences from ionizing radiation.
Conclusion
CT scan is an excellent example of how veterinary medicine is evolving to better serve our beloved pets, this technology can definitely be a game changer if used in a proper way. Embracement of this technology in veterinary diagnostics can uncover hidden health issues, improve treatment outcomes, and give our pets the best possible life.
References:
- Kistler JP, Hochberg FH, Brooks BR, Richardson EP, New PF, Schnur J., 1975. Computerized axial tomography: clinicopathologic correlation. Neurology, Mar; 25(3):201-9.
- Ambrose J. Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography), 1973. Clinical application. British Journal of Radiology, Dec; 46(552):1023-47.
- Adelaide Greco, Leonardo Meomartino, Giacomo Gnudi, Arturo Brunetti, Mauro Di Giancamillo, 2023. Imaging techniques in veterinary medicine. Part II: Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, nuclear medicine, European Journal of Radiology, Volume 10, 2352-0477.






Be the first to comment