Introduction
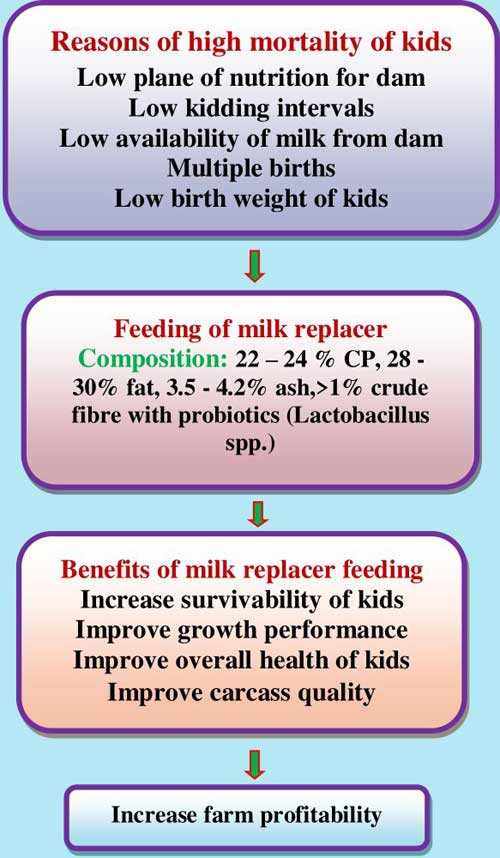
Goat farming has a significant part in raising income, work, capital storage and enhancing human nutrition. It gives daily bread and butter to for nearly 38 million animal holders like woman’s, landless laborers’ and marginal farmers who hold out in interior areas & don’t have any other way of support. In domestic animals, goat plays a predominant part in the small animal production system and the lifetimes of the landless peasantry (Shahjalal et al., 2000). Goat rearing is a subsidiary income source for rural poor along with agriculture (Nandi et al., 2011). Goats are among the main core-raising animals in India and goat meat (Chevon) faces huge domestic demand, with no social, ethnic, and religious restrictions, thus sharing significant contribution to the national gross domestic product (GDP). Goat farming is a preferred option among the small and marginal farmers (those having less than one hectare of land) or landless farmers who depend on common grazing and forest land for fodders. In the long run, the overall productivity and profitability of the farm are determined by the health and growth rate of kids (Kabir, 2003). Milk is the most important and nutritious food required for survival and normal growth of kids. High kid’s mortality is taken as one of the most significant problems of goat production in rural areas (Uddin et. al., 2003). Relatively low birth weight, lower body weight gain and an inadequate feeding of dams’ milk are the major affecting factors that are related to higher death of kids (Miah G. 2003). These factors have together created a big demand for the availability of an alternate to dam milk like milk replacer. This has posed a challenge cum opportunity in front of the scientific community to develop a feeding regime for kids; so that the kids can be fed sufficiently to meet the nutritional requirement for the survival and growth during their early stage until they can go for grazing (Dutta et al., 2006). As we know, feeding is very important nutritional management practice and has profound impacts on mortality, morbidity and growth of the young kids. Sufficient and good supply of various nutrients for kids through a liquid feed (milk or milk replacer) is essential for their performance and welfare (Bugati et al., 2010). Milk Replacers are very good sources of liquid feed for kids. Thus, its provision can be a cost-effective strategy for saving kids’ life as well as obtaining higher growth rates from them.
Composition of Milk Replacer
The protein, fat, sugar and crude fibre are the important nutrients with the high variation in the milk replacer composition of goat kids given by different researchers. The fat content of milk replacer should be the same as the fat concentration of goat milk. Milk replacers containing 20-28% protein and 16-24% fat have been well used by goat kids (Morand-Fehr, 1981). Almost similar performance to normal milk-fed kids can be gained in kids fed milk replacers containing 22 – 26% protein and 20% animal fat (Teh et al., 1985). Acidified milk replacer having 28 – 30%, 22 – 24 % CP and 3.5 – 4.2% ash resulted in a similar bodyweight increase that of kids received goat milk (Sahlu et al., 2006). Feeding of milk replacer having 24% crude protein is advisable while the addition of probiotics (Lactobacillus spp.) can turn out to be a better feeding regime. A total solids concentration of 14.3% of obtained by adding 20% animal fat was acceptable. Total Solids contents in the dissolved milk replacer should range from 12 to 15 %. Milk protein is more favourite to plant protein or other animal protein for constituting milk replacers. Crude fibre is a good index of plant protein in milk replacer. Normally, milk replacer containing less than 1% crude fibre, is considered as a good quality milk replacer.
Survivability of kids by milk replacer feeding
Mortality of kids is the main problem in goat farming because goats are very low milk producer that milk is sufficient for the kids so milk replacer is best to alternate to fulfil the kid’s requirement. Milk replacer feeding to pre-weaning kids observed, feeding 24% crude protein, milk replacer is useful to reduce the mortality of the kids and thus can be used safely for early growth. Similarly, Sultana et al. (2014) reported milk replacer prepared using Shoti (Curcuma zedoaria) leaves gave higher survivability as compared to receiving whole milk. Thus, milk replacer gives better survivability than other kids who gets insufficient milk due to multiple births. Mortality rates can be lowered even up to 0% by using milk replacer was evident in milk replacer feeding studies by Bhatta et al., 2018. So, the majority of the studies are advocating towards feeding milk replacer to reduce mortality problems in the goats’ kids.

Effect on growth performance by milk replacer feeding
Due to multiple births and low yield of milk, the child of the goat does not obtain a sufficient quantity of nutrients. Adequate nutrient supplies hamper/reduce the growth of kids. For the proper growth and to fulfil the requirements of kids, milk placer can be the best alternative. Ali et al., (2016) also noted the difference in final body weight between kids managed on milk replacer and whole milk, but in case of insufficient milk supply, milk replacer can be an efficient option. Goat kids feed with milk replacer prepared using Shoti (Curcuma zedoaria) leaves showed better dry matter intake and average daily gain also digestibility of dry matter and organic matter in replacer fed groups were higher. Feeding of milk replacer is affecting feed conversion ratio, weight gain and nutrient use, therefore, Shoti leaves milk replacer can be used for goat kids as an alternative to goat milk. Kids fed whey-based milk replacer comparisons with a commercial milk replacer showed higher dry matter intake, better dry matter conversion efficiency and higher average profit. So, on a sufficient supply of milk replacer kids’ shows growth rates comparable to milk-fed kids while on supplementation along with milk shows higher growth rates.
Effect on the overall wellness of the kid by milk replacer feeding
Feeding of milk replacer also improves the overall health of kids. Ammonia concentration decreased and total volatile fatty acids increased with milk replacer feeding in both milk replacer and milk replacer with probiotics. Feeding of milk replacer in kids improved the nutrient digestibility. So, feeding of milk replacer during pre-weaning has an effect on feed efficiency, weight gain and nutrient use. The rumen fermentation pattern is not at all adversely affected and kids showed healthy status due to milk replacer feeding in kids. On the other hand, if the milk replacer powder contains added probiotics, then it has added beneficial effect on health and growth performance of kids (Dutta et al., 2006). Feeding of a milk replacer has probiotics (Lactobacillus spp.) appears to be supporting gastrointestinal health through positive microbial balance and reduces weaning stress thereby enhances overall animal production. Ragionieri (2016) observed that medium and short-chain fatty acid supplementation in milk replacer could better regulate epithelial cell proliferation. It may be an “emollient effect” that leads an easier “peeling” so might improve the efficiency of nutrient transfer across the epithelial tissue. Ciliate protozoa population in the rumen, decreased in milk replacer powder fed kids than in natural milk-fed children, also the ammonia concentration decreased and total volatile fatty acids increased with milk replacer feeding.
Effect on carcass characteristic by milk replacer feeding
Quality of nutrition supplemented, in the first phase of life may an important role in changing the carcass character of finisher animals for more market value. Milk replacer included coconut oil, powdered skimmed milk, fat, cereal products and by-products, have a marked effect on the fatty acid composition and quality of meat. Milk replacer diets improve the water/protein proportion in the muscle. Feeding milk replacer provides more intense characteristic goat meat flavour and odour more juiciness and tenderness as compared to natural diets. Milk replacer energy supplements in the form of crushed linseed and calcium-soap during the post-weaning has a useful scheme for making more body weight. Kids, fed milk replacer added with conjugated linoleic acid diet give better growth rate, higher commercial carcass yield and net carcass yield and better meat quality. Therefore, it is rather clear that milk replacer feeding proves to be beneficial as it bears on different attributes of carcass characteristics and overall carcass quality positively.
Effect on economics by feeding of milk replacer
A milk replacer for kid rearing can be profitably used in goat rising without any negative effects on kid growth. As well, it increased farm profitability based on milk price and the body weight of kids. Dutta et al. (2006) found in their study that the replacer with 24% crude protein was also found economical when compared to the price of goat milk when they supplemented kids with milk replacer added with probiotic (Lactobacillus sporogens). The cost of milk Replacer given to kids groups is less than the cost of raw milk. Milk Replacers are cheaper than whole cow milk and milk replacers are an excellent beginning of nutrition for kids and they don’t hold the risk of waste milk. Kamalahasan et al. (2018) by his study concluded, raising of animals on formulating milk replacer feeding is a safer choice for the farmer to decrease the price of goat rearing. The replacer with 24% crude protein is economical when compared to the price of goat milk the cost of after reconstitution was 4.43 rupees/lit. (Dutta et al., 2006). The milk replacer has positive effects on survivability as basically it provides various required nutrients in enough amount to the kids. It also yields better performance related to weight gain, dry matter intake and feeds conversion efficiency. Majority of milk replacers formulated using locally available stuff thus proved an economical strategy for rearing kids.
Conclusion
Milk replacer is very much essential part of kids nutrition, which ultimately controls early age mortality and thus lifetime performance as good. A milk replacer is a unique source which plays a vital role to bridge the gap in the need for nutrients by rapidly growing kids and their supply through milk. Feeding of milk replacer is cost-effective for farmers so increases the overall farm profitability.
Reference: On request.







Thanks for the wonderful article..could you suggest any milk replacer for goat ?Will it avaliable in india ?