Introduction
Phospholipid (PL) is ubiquitous and is essential for the lipid bilayer of cells. Phospholipids are lipids containing phosphorus, a polar potion, and non-polar potion in their structures. Phospholipids are amphiphilic molecules with a hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head group Phospholipids (PL) are common and important substances in the biological world Phospholipids found in most cell membranes are Glycerophospholipids and Sphingolipids Consists of fatty acids esterifies to a glycerol backbone, a phosphate group and a hydrophilic residue
Significance of phospholipids
The structural and functional properties are pivotal for the survival of the cell. A phospholipid is an essential molecule that is found in the cellular membrane. Phospholipid (PL) are common and important substances in the biological world.They make up the membranes of most cells in both plants and animals These lipids are organized in double-layer structure serving as barriers between the various compartment and providing the proper environment for receptors, enzymes, and transport proteins. They also act as a platform for communication between cells and for hormones that regulate cell functions.
Milk contains Pl in the milk fat globule membrane (MFGM). The phospholipid is amphiphilic molecules of moderate hydrophilicity. Phospholipids are the modified triglycerides with two fatty acids group and a phosphorus group main component of cell membrane. Phospholipids may be dividing into two groups: Glycerophospholipids and spingophospholipid. The phospholipid is commonly found in natural and synthetic sources. Naturally found in almost Egg yolk, Soybean, Peanut, Milk and other milk products phospholipids are essential molecules that are found in cellular membranes. A cell in the human body cannot function normally without the presence of these phospholipids. As the name implies, phospholipids are made of the combination of lipids (fats) and the mineral phosphorus. These lipids are fundamental components of the cell membranes which are essential for growth, maturing and proper functioning of cells. The structure and function of the cell membranes are of essential importance for human health. Phospholipids are found in higher concentrations in soy, eggs, marine sources and the brain tissue of animals. Phospholipids are the most important, nutritionally important constituents of soy lecithin. Lecithin with phospholipids can support a general reduction of the serum plasma cholesterol levels phospholipids are in demand from the food supplement industry in the interest of the consumers. Soya phospholipids are regarded as versatile and functional ingredients of food. Powdered Lecithin (LECIVA S25P) is used mainly for the production of food supplements in the form of tablets, hard gelatin capsules or nutritional premixes. Granular Lecithin (LECIVA S25G) has also proved to be an effective and convenient form of administration around the world for many years since it can be consumed directly as a supplement or sprinkled on salads. A health claim has been formulated for de-oiled lecithin (mixed phospholipids):”Deoiled soy lecithin may have Phosphatidylcholine has been used successfully to treat liver diseases supported by various clinical studies. The most frequent of these are acute and chronic cirrhosis of the liver, fatty degeneration of the liver (steatosis, fatty liver) and liver damage from alcohol, chlorinated hydrocarbons, medicines, etc. In cases of previous liver damage phosphatidylcholine has brought about a marked improvement in the speed of recovery by repairing the cell membrane, renewal, or regeneration of liver parenchyma.
The beneficial effect of phosphatidylcholine on the liver is connected with its role as a central building block in the cell membrane. Phosphatidylcholine is of great importance for the structure and the functioning of the membrane systems of all body cells. Without PC, the cell membranes would harden, prohibiting important nutrients from entering and wastes from leaving the cell. Neurological disorders arising from a deficiency of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine can be treated by increasing the plasma choline level by oral administration of phosphatidylcholine in capsule or tonic forms. Soya phosphatidylcholine (LECIVA-S35) is a natural precursor of choline and thus of the synthesis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. An increased rate of synthesis is generally associated with an improvement of memory and muscle function. In 1998, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) of the US National Academy of Sciences identified choline as an essential nutrient and recommended daily intake amounts. And, in 2001, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a nutrient content claim for”Soya Phosphatidylcholine helps to maintain a healthy cholesterol level from foods providing 1.2 g/day”. Eggs are a major source of phospholipids (PL) in the Western diet. Dietary PL has emerged as a potential source of bioactive lipids that may have widespread effects on pathways related to inflammation, cholesterol metabolism, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) function. Based on pre-clinical studies, egg phosphatidylcholine (PC) and sphingomyelin appear to regulate cholesterol absorption and inflammation. Phospholipid products in the crude or refined or modified form are used for wetting, emulsification, in feed and food products and also in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Phospholipids also exhibit technological functions that are of industrial impotence of feed products. These functions enable them to serve as emulsifiers, wetting agents.Positive outcomes from double-blind trials, backed by hundreds of clinical studies and thousands of experimental studies, establish PS, PC, SM, and mixed phospholipid functional benefits for the brain, liver and circulation The functional phospholipid are extremely well-tolerated and pose no toxic effects.
Sources of phospholipids
Commercially available Phospholipids
Phospholipids the essential for a healthy life
- Main phospholipids present in soy lecithin are phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphatidyl acid (PA).
- Soya phospholipids are regarded as versatile and functional ingredients of food. Used for the production of food supplements.
- Lecithin with phospholip ds reduces the serum plasma cholesterol levels
- Liquefying effect of this cholesterol reduction rejuvenates cell membranes
- Phosphatidylcholine: Phosphatidylcholine has been used to treat liver diseases
- Acute and chronic cirrhosis of the liver, fatty degeneration of the liver (steatosis, fatty liver) and liver damage from alcohol, chlorinated hydrocarbons, medicines
- Phosphatidylcholine is of great importance for the structure and the
- the functioning of the membrane systems of all body cells
- Neurological disorders arising from a deficiency of the neurotransmitter
- acetylcholine can be treated by increasing the plasma choline level
- Soya phosphatidylcholine is a natural precursor of choline and synthesis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
- Improvement of memory and muscle function
(Institute of Medicine (IOM) of the US National Academy of Sciences, 1998 and FDA., 2001)
Milk -Phospholipids and its constituents
- Milk lipids have 3 to 5 % (w/w) fats
- Milk phospholipids have two classes Glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids
- Milk contains PL in milk fat globule membrane (MFGM)
- Phospholipids are mainly localized in MFGM- 60%–70% phospholipids
- Representing about 1% of the total milk lipid fraction
- Fat globules of milk are surrounded by a membrane, triple layer of phospholipids
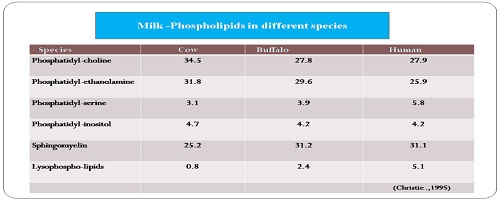
- Milk phospholipids differ in compositions from soybean lecithins and egg lecithins particularly for the content of two bioactive phospholipids Sphingomyelin – 24%, Phosphatidylserine -12%
- Triglycerides 97% – 98% of total milk fat (Parodi., 2004)
- Lipids are present in the form of milk fat globules diameter 4 to 5 µm
- Fat globules Surrounded by a biological membrane known as the milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) (Lopez et al., 2011)
- Highly complex biological membrane and Trilayer structure
- MFGM is composed of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, and phosphatidylserine (Martini et al., 2016)
Milk -Phospholipids in different species
Conclusions
- Phospholipids are endogenous substances
- Phospholipid content of milk varies from 20-40 mg /100 gm milk
- Stabilize the suspension of milk fat in the aqueous environment
- Phosphatidylcholine, Phosphatidylethanolamine, and Sphingomyelin are the major polar lipids in bovine milk. and represent 25-35% of the phospholipids
- Lecithins are most often used as amphoteric emulsifiers
- Egg PL appears to influence hepatic lipid metabolism through effects on cholesterol and bile acid synthesis
- Egg phospholipids may lessen the risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD)
- Reducing lipid absorption (PC, SM), reducing hepatic lipids (PC, SM),
- Increasing HDL cholesterol efflux (PC, SM), and reducing inflammation
References
- Institute of Medicine (US). Food and Nutrition Board, 1998. Dietary reference intakes: a risk assessment model for establishing upper intake levels for nutrients. National Academies Press.
- Tang, W.W., Wang, Z., Shrestha, K., Borowski, A.G., Wu, Y., Troughton, R.W., Klein, A.L., and Hazen, S.L., 2015. Intestinal microbiota-dependent phosphatidylcholine metabolites, diastolic dysfunction, and adverse clinical outcomes in chronic systolic heart failure. Journal of cardiac failure, 21(2), pp.91-96.
- Jaiswal, P., Jha, S.N., Borah, A., Gautam, A., Grewal, M.K. and Jindal, G., 2015. Detection and quantification of soymilk in cow–buffalo milk using Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (ATR–FTIR). Food Chemistry, 168, pp.41-47.






Be the first to comment