Introduction
Training is an important and integral part of human resource development (HRD) and is crucial to organizational effectiveness. Training helps individuals to prepare for change to face the challenges. Training helps individuals to acquire competencies necessary to achieve organizational objectives. Human resource management has two basic approaches- a reactive, or problem-solving approach; and a proactive, or forward-looking approach. Training is used in both.
Training is a systematic process of changing the behavior through change in knowledge, skill and attitudes of present farmers to improve the match between farmer characteristics in farming and livestock rearing requirements. Improvement in knowledge and skills for doing a particular job. Training bridges the gap between job, needs and farmer skills, knowledge and behaviors.

What is training?
According to Edwin B. Flippo (1984) “Training is the act of increasing the knowledge and skill of an employee for doing a particular job”
According to Micheal J. Jucious “Training is a process by which the attitudes, skills and abilities of employees to perform specific jobs are increased”
According to E. F. L. Breach (1947) “Training is the organized procedure by which people learn knowledge and/or skill for a definite purpose”
According to William G. Torpey (1959) “Training is the process of developing skill, knowledge, habits and attitudes in employees for the purpose of increasing the effectiveness of employees in their present government position as well as preparing employee for future government positions”
What is Need for Training?
- To improve the efficiency of farmers.
- To reduce wastage of time and money.
- To bring down supervision.
- To achieve optimum performance.
- To boost morale of farmer.
- To prepare workforce for future challenging work.
- To reduce absenteeism.
- To build career by personal growth.
Objectives of training
- To increase the knowledge of farmer in doing specific livestock rearing system.
- To impart new skills among the farmer systematically so that they learn quickly.
- To bring about change in the attitudes of the workers towards fellow workers, supervisor and the organization.
- To improve the overall performance of the organization.
- To make the farmer handle materials, machines and equipment efficiently and thus to check wastage of time and resources.
Important characteristics of training
- Training must help to create an attitudinal change by creating awareness of the overall process.
- It must enhance skills in organizational and managerial areas.
- An effective training programme should be flexible.
- A good training performance should prepare the trainee mentally before they are imparted any job, knowledge or skills.
- Training programmes should be conducted by well qualified and experienced trainers.
Training Methods
- As per Bernardin and Russel, training methods can be divided into two categories
Primarily informational or transmittal in nature – They use primarily one way communication in which information is transmitted to the farmers. Some of the major methods are: lecture, audio visual, independent study, programmed instructions.
Experiential in nature – That is the farmer interacts with the instructor, a computer/ simulator, or other trainees to practice the skills. Some of the major methods are – on the job training, computer based training, simulation, games, case analysis, role playing, behavior modeling and sensitivity training.
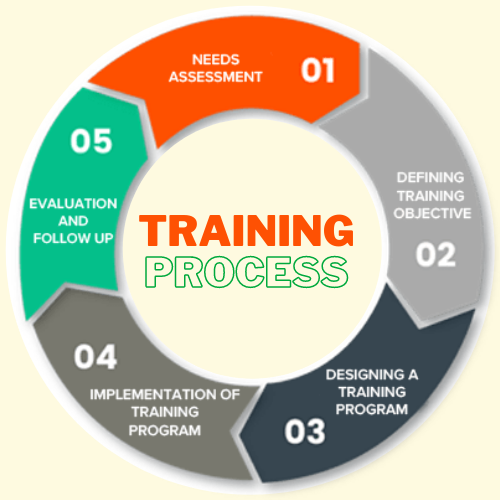
1. Training Needs Assessment (TNA)
The first step in the training process is to assess the need for training the farmers. It analyses what are the long term requirements of the farmers and what does the organization expects from the farmers. If there is a mismatch between the skills and knowledge required, it means there is a learning gap.
To assess this learning gap below three elements is closely examined:
Training Needs = Desired Capability – Current Capability of the Participants
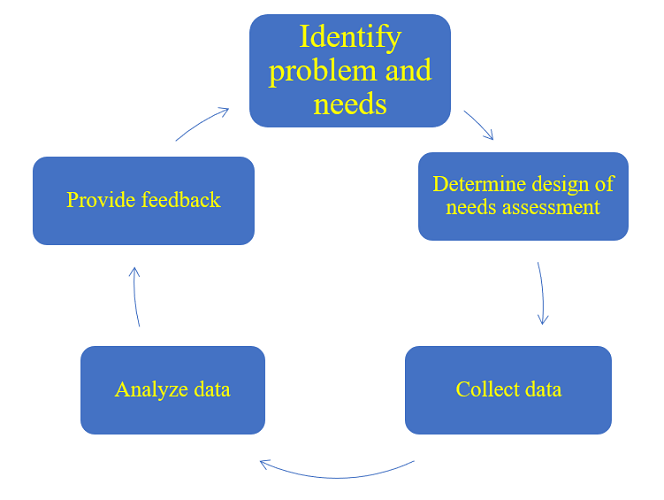
A. Identify problem and needs: The first step in TNA is to identify problems and needs. Before TNA is conducted, it should be probed whether training is needed. In the public sector, it is important to identify organizational context in such aspects as policy, goal, roles and responsibilities. Realizing the policy direction of the organization, performance analysis known as “gap analysis” is conducted to look at an official’s current working performance and knowledge and identify whether an official is performing as desired based on given roles and responsibilities. Then the more explicit the standard for current performance and knowledge, the easier it will be to describe the gap in performance or knowledge deficiency.
B. Determine design of needs assessment: The second step in TNA is to determine the following:
- Target groups to be trained
- Interviewees
- Survey methods
- Survey plan including schedule to be conducted TNA and persons in charge of TNA.
-
- Those items become the basis for a training course designer to either create a new training course, identify an existing one that can fulfill the need, or obtain one externally.
- The survey must clearly define the target group of the training, i.e., target population. Although no strict rules for defining exist, the target population must be defined in line with the objectives of TNA.
C. Collect data: The third step in TNA is to collect data through:
- Reviewing documents on existing training (secondary data and information)
- Conducting survey including interviews and observation at work.
-
- It is important to collect and review secondary data and information prior to conducting interview surveys.
D. Analyze data:
- Organization analysis: The objectives of the organization are studied. The end result that a farmers wants to achieve is examined in context to how it uses its resources to achieve the same. Organizations’ internal and environment is also considered.
- Operation Analysis: A job requires a combination of different activities for successful completion. Operation analysis focuses on the needs, skills, knowledge, and attitude required to efficiently complete the job. Person analysis
- Person analysis: In-person analysis the focus is on the farmers who has to perform the job. It is analyzed whether the performance of the farmers is satisfactory and he is being able to achieve the organizational goal.
E. Provide feedback: The fifth and final step of TNA is to provide the training committee members and concerned officials with feedback on the survey results, then to receive the members’ comments to reflect on the report.
In the group discussion among the training committee members, it is important to clarify the following points.
- Are there any other important findings?
- What are other suggestions to improve the methodology for the next TNA?
- Is there any recommendation for the training course in such aspects as participants, methods, module and curriculum, and schedule?
- After finalizing the report, the training committee members discuss and determine the next steps for training preparation.
2. Defining Training Objective
After deriving the learning gap organizations should define the learning objective.
- Goals and objective of training becomes the foundation of the training initiatives.
- Hence determining the training objectives gives a direction to the entire learning program.

3. Designing a Training Program
Once the objective of the training program is determined, it is time to analyze the factors that need to be considered while designing a training program. Well-designed training is planned, appropriate to the target audience, and able to be delivered within the resources available. Strategies and methods in this section address planning for training, developing the materials used in providing training, and crafting a strategy for evaluating training.
4. Implementation of the Training Program
Refers to putting the training plan into action. There should be a proper environment created which is helping to learning. It should be preferably a participative approach and trainer should promote role-playing and interactive games to keep the trainees involved. The training should be presented so that its organization and meaning are clear to farmers.
An effective training program allows farmers to participate in the training process and practice their skills and/or knowledge. For making the training program effective, the targeted group of farmers and the use of methods such as on-the-job or off-the-job training should select first. The capacity and knowledge of trainers and their acceptance by the participants are of secondary importance.
On the job: Training is administered at the actual work site using the actual work equipment.
Off the job: Training is administered away from the actual work site. It may be any prominent hall room or auditorium, but the required training environment equipment and materials should be available or arranged.
5. Evaluation and Follow up
Training evaluation is done to check whether the goals and objectives of the training have been achieved or not. Feedback needs to be taken from the participants on the training results.A follow up can be done by asking the supervisors whether the participants are applying the skills learned in the learning program on their day to day job.
A. Participants Opinions: Evaluating a training program by asking the participants’ opinions is an inexpensive approach that provides immediate response and suggestions for improvements.
-
- The basic problem with this type of evaluation is that it is based on opinion rather than fact. In reality, the trainee may have learned nothing but perceived that learning experiences have occurred.
B. The extent of Learning: Some organizations administer tests to determine what the participants in the training program have learned.
C. Behavioral Change: Tests may accurately indicate what has been learned, but they give little insight into desired behavioral changes.






Be the first to comment