In India, animals are reared for daily-hoods as well as income purpose. The cattle is source of income to the small scale farmers and also increases the health and economy of the farmers. Desi cattle reared for dual purpose such as milking, breeding and farming purpose. Some desi breeds are resistant to heamoprotozoal diseases. Most of the farmer rear the cattle in small hut and they feed the grass and left to forest for grazing. Some of the toxin plants such as Aconite, Horse chestnut, buck eye, corn cockle, onions, pig weed, dogbane, milkweed, rape, cabbage, turnips, broccoli, celandine, downy, lupine, alfalfa, lucerne, yellow and white sweet clover, bracken fern mayapple, black locust, sorghum, horse brush etc causes toxicity to the cattle. Excess intake of plants also causes toxicity to animals. Among vegetable plants Genus Allium content the onion and garlic. Excess intake of onion plant causes toxicity to the cattle.
The India is the second largest onion growing country in the whole world. The major onion producing states are Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odessa, Jharkhand and Telangana.

Pathophysiology of Toxicity of Plant
Onion belongs the plant Genus Allium. Cattle are more susceptible compared to sheep and goat. The onion whole plant poison to the cattle and buffaloes. When Cattle grazes in the field, the plant enter into the rumen converted to n-propyl disulphide, allyl propyldisulphide and allyl sulphide with the help of the rumen microbes. n-propyl disulphide, within erythocyte depletes the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase because of this the glutathione remain in the oxidised state. The oxygen particles react with Thiol free radicals and denature the hemoglobin and precipitate with the cell membrane causing the formation of the Heinz bodies. These Heinz bodies are lysed and inducing hemolytic anemia. Where as free radicals oxidised hemoglobin to methhemoglobin. The amino acis content in the onion plant is S-meth and S-prop(en)yl cysteine sulphoxide (SMCO). The SMCO hydrolysed in the rumen and converts to thiosulphate and further metabolized to dipropyl disulphides and dipropenyl disulphides. These end products are hughly toxic to erythrocyte causing hemolysis. These onion plant induces hemolytic anemia and causing decreased in hemoglobin concentration. The death may be due to hemolysis and causing anemia.
Clinical Sign
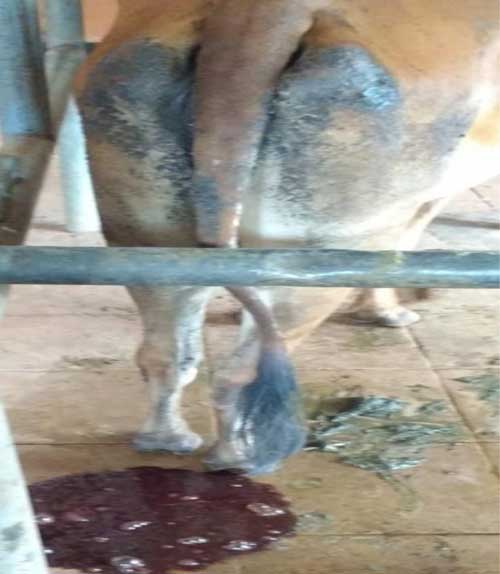
Desi cattle shows the clinical signs after ingestion of onion plant such as dull, depressed, pyrexia, inappetance, dyspnea, jaundice, pale conjunctival mucous membrane, coffee colour urine, dark fecal output, constipation and sometimes death due to hemolytic anemia. Sometimes abortion also occur in pregnant cattle.

Diagnosis
- Based on history of the ingestion of the onion plants, sometimes feeding of onion leaves, onion
- Based on clinical signs showed animals commonly inappetance and dark coffee colour urine,
- Hematological findings: decreased hemoglobin content, total erythrocyte count and packed cell volume and macrocytic hypochromic anemia indicated by Erythrocytic indices. Some times leukocytosis occur. On Staining of thin blood smear there was the Heinz bodies observed.
- Based on serum biochemistry:
- Based of postmortem: Commonly onion odor in the rumen and flakes of the onion plant found in the rumen and coffee colour dark urine observed in the urinary bladder of the cattle.
Differential Diagnosis
- Babesiosis- tick infestation on the body, high fever, cross breed are most affected compare to desi breed
- Postparturient hemoglobinuria – phosphorous dificincy, history of calf born
- Bacillary hemoglobinuria- occurred due to Clostridium haemolyticum
- Leptospirosis
- Enzootic bovine pyelonephritis
- Chronic copper poisoning
- Animal bites also causes hamoglobinuria
- Cold water intake- excess of cold water intake causes haemoglobinuria which mainly occur in calves
Treatment
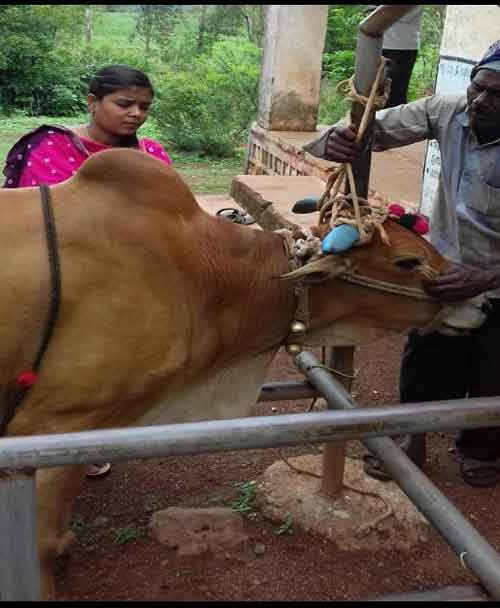
- The affected animal treated with antioxidants such as vitamin E and selenium combination 1ml/25kg B.wt. Intramuscular for 3-5 days along with supportive therapy such as intravenous fluid therapy and gut transplantation for the improvement of the rumen microbes.
- Phosphorus content injection also help in early recovery of the animal.
- Blood transfusion helps to fast recovery.
- Oral antibiotic given to the reducing the ruminal anaerobic bacteria which helps in the formation of the oxidative substances.

Management
- The extension activity to the farmers about the awareness of the toxicity of onion plant to the animals should be conducted.
- The excess rotten onion plants and whole onion should not feed to the animals
- The rotten onion plants in the field should be buried or burn in the side of the farm
- If any animal accidentally ingest the excess amount of onion then immediately contact to near by veterinary hospital for further treatment
- The affected animal should immediately feed the sodium bicarbonate powder for maintain the pH and commonly antioxidant such as selenium vitamin e supplement should be given
Reference:
- Onion toxicosis in buffaloes, N.A. Patil et. al. Buffalo bulletin (2019) vol.38 No.2
- Vikaspedia.in
- Fatal onion (Allium cepa) toxicosis in water buffalo, Vanessa Borelli et.al. J.Vet. Diagn. Invest (2009) vol 21:402-405
|
The content of the articles are accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge. It is not meant to substitute for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, or formal and individualized advice from a veterinary medical professional. Animals exhibiting signs and symptoms of distress should be seen by a veterinarian immediately. |





Nice information
Nic
NYC one
Very informative and good
Nic article