Abstract
The motive or purposes of the study is to know the causes of still birth in animals and this is related with production in animal kingdom. Mismanagement as well as exogenous and endogenous causative agent and nutritional factor are equally responsible for still birth. In case of domestic animal, lactating animal breed are having more risk of still birth and on the other hand wild or zoo animal faces this problem due to either placentitis or other non-infectious causes. Dystocia and other difficulties during parturition may be cause of still birth. So, our aim to minimize the problem by putting effort by adapting various ways.
Introduction
“Still Birth” the term is more or less accustomed by veterinary as well as medical doctors. It is a situation when the mature foetus is expelled at dead condition or die within 24-48 hours after parturition. The incidence of still birth is more in primiparous (during 1st calving) and multiparous (having more than one calf) animals. It causes huge economic loss for those people who are fully dependent on their livestock. It has been shown that ruminants with still birth incident having more risk of endometritis or retention of placenta (ROP).
Brief discussion on female reproductive system
“Theriogenology ‘is the study of reproductive system both physiology and anatomy of the reproductive system. Reproductive system provides all the hormones that allows the physical change and helps in adaptation. In breeding management programme, the reproductive system is manipulated which allows the quick alteration in productivity of animals.
The system includes:
- Ovaries: production of ovum and two reproductive hormones estrogen and progesterone.
- Oviduct (fallopian tube): funnel shaped structure. It captures ovaries.
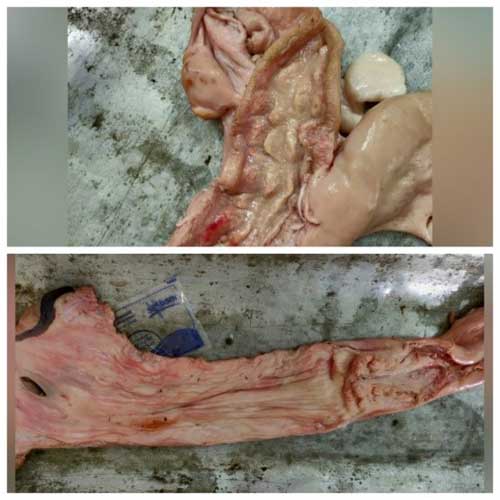
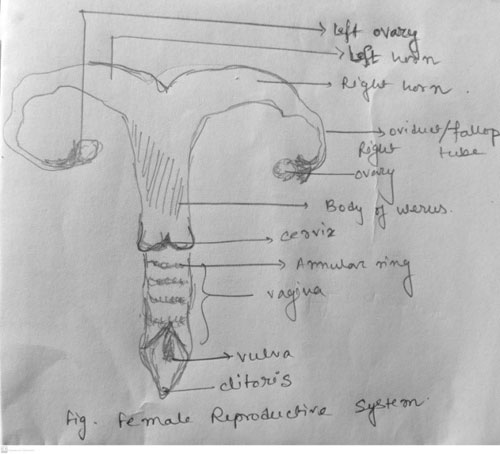
- Uterus: Uterine horn is long and the embryo moves from oviduct to uterine horn and the embryo starts to develop here.
- Cervix: It has thick wall and annular ring and it’s the passage of sperm during mating.
- Vagina & Vulva: Vagina is a hollow organ that accept or receive the male’s penis.
Causes of still birth
Non-infectious causes
- Dystocia: It means difficulty in parturition. Size of pelvic inlet always matters. Animal with small sized pelvic canal, fetal mal position, twin, uterine inertia, and uterine torsion causes Dystocia which leads to still birth.
- Congenital defect.
- Heat stress: More temperature of mother due to pyrexia causes heat stress to foetus.
- External administration of PGF2α, corticosteroid.
- Lack of proper nutrition which essential for placental and fetal development
- Number of off springs: usually the animals during their first calving and the animal giving birth more than one offspring go through the problems of still birth.
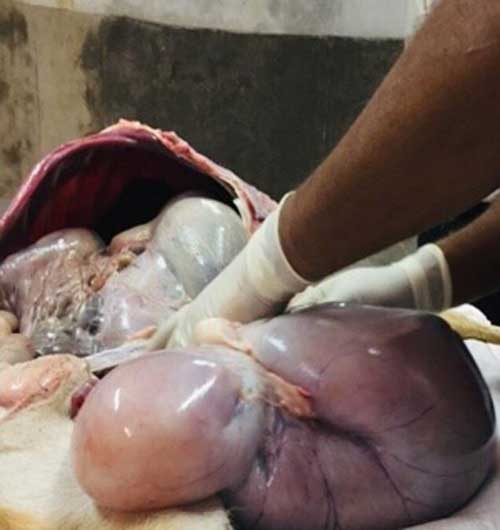
Infectious cause
- Viral disease: Bovine viral diarrhea (bovine herpes virus 1), Blue tongue in sheep, Infectious Bovine Rhinotrachitis (IBR), Equine arteritis virus are responsible for still birth.
- Bacterial disease: Listeriosis, Leptospirosis, Campylobacteriosis, and Brucellosis often results still birth.
- Protozoan disease: Trichomoniosis.
Risk factors
- Environmental factors.
- Genetic & non genetic factors.
- Shorter or Prolonged gestation period- miscalculation of gestation period of the dam increases the risk of still birth.
- Breed of the animal.
- Age of the animal.
Management or control of still birth
Still birth is an unexplained thing to us. Why or how it is happened is still not properly explained in some cases. So we have to manage this. Management is utmost important part for reduction of incident of still birth and keeping the animal healthy.
- Obstetric care: During pregnancy, the dam should be taken care and properly fed.
- Vaccination: Animal should be vaccinated against some diseases like IBR, BVD and Leptospirosis.
- Bio-security: Maintenance of bio-security of the farm. In the farm. The newly imported animals should be quarantined. Farm visitors and workers should be careful about spreading of diseases from one animal to another animal.
- In an organized farm record keeping also helps to control still birth.
- Rodent or any other vector control measures should be taken as rat urine is the source of Leptospira.
Conclusion
There is saying that ‘prevention is better than cure’. Not only still birth but also other diseases causes disaster to the livestock as well as whole animal kingdom. Maintenance of animal health and vaccination of animal in proper time can reduce the possibility of still birth in animals.
Reference
- The Merck Veterinary manual.
- A Text book of veterinary preventive medicine by Amalendu Chakrabarti
|
The content of the articles are accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge. It is not meant to substitute for diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, prescription, or formal and individualized advice from a veterinary medical professional. Animals exhibiting signs and symptoms of distress should be seen by a veterinarian immediately. |






Good
खुप छान माहिती मिळाली.धन्यावाद.
Very nice and informative
Awesome. Points are absolutely right…