Introduction
Rabies is one of the Neglected Tropical and Zoonotic Disease (NTDs) that is almost always fatal. It is practically 100% preventable, but worldwide 55000-60000 person die due to rabies of which one third is from India alone. 97% of these cases are following bites i.e., dog mediated rabies. One death occurs for every 9 minutes. The studies indicate 99% of animal mediated rabies death occurs in Asia and Africa. India accounts 65% of human rabies death in Asian continent, approximately 20,000 deaths per year. Only a few countries in Asia (Japan, Taiwan, Hong Kong, South-Korea, Malaysia and Singapore) were on the rabies free zone track due to effective preventive strategies like mass dog vaccination and animal birth control programmes. For several tropical diseases, the Global burden of disease (GBD) figures are thought likely to be underestimated of the current disease burden. Vaccinating 70% of the dogs in an area is needed for herd immunity. In this essay some of the ideas or strategies to reach the goal of zero by 2030 was discussed. Following the mass vaccination , PEP for humans, enhancing the mission rabies program will definitely guide India to reach the target zero rabies. Reaching zero by 30 will save lives of children and livelihood of adults. Rabies is 100% preventable the time to act is now.

Constraints present in India
The Lack of due concern among the Medical, Veterinary & other related Professionals and lack of social awareness among the people are the major reasons for increased burden of rabies cases in India. Doctors said that high number of rabies deaths is due to low proportion of vaccinated dogs. Also due to stable increase in stray dog population and lack of animal birth control programme plays significant role in case burden of rabies. Intersectoral-coordination and communication which is essential for rabies control is an ongoing challenge in India. Even the Pet owners needs a proper guidance about Annual Vaccination of their Pets. Veterinary Dispensaries all over the nation should be equipped with Anti-rabies Vaccine doses with sufficient storage facilities to prevent rabies in nook and corner of this nation. The Animal owners also should be taught about the precautionary measures on Post-exposure Dog bite and other Prophylactic measures.

Steps being undertaken in India
- The control of dog Rabies presents a Unique and Challenge undertaking. India has called for a National conference on 2016 by APCRI ( Association for Prevention and Control of Rabies in India) to support and work for accomplishing the Global Target of Rabies elimination by 2030. The recommended strategy is “One Health Approach” that involves an effective coordination and cooperation of the Medical ,Veterinary and other related sectors. Pilot programs for rabies control have been commenced in States like Tamilnadu and Haryana.
- Certain Animal Welfare Organisers like WVS India also take measures like Mass Vaccination of dogs and Animal Birth Control Programmes which played a significant role in war against rabies control in India.
- Mission Rabies: International volunteers from 14 countries joined forces with local dog catchers and vets to make this campaign a huge success, not only protecting so many dogs from Rabies, but increasing awareness and making Rabies a country-wide issue. Reaching our target of 50,000 dogs in just 25 days, Mission Rabies made a difference in a short space of time in the world rabies hotspot India.
- SARAH (Sikkim Anti-rabies and Animal Health Programme) initiative is a successful program being taken in the state of Sikkim. It is the first state wise rabies program in India and demonstrated a successful one health model which is directed towards Canine vaccination, Humane dog population control, Community Education, Treatment of Sick and Injured animals. It is State Government supported programme also funded by the International NGOs. It is a Model of Rabies control in a Predominant Rural environment with limited resources.
Feasibility of rabies elimination
The less reproductive number R0, key parameter test to undertake the effective control interventions lie between 1 and 2, this low value suggest that rabies can be easily controlled through mass dog vaccination. Reducing the dog density through indiscriminate colouring is highly likely to be ineffective.
What shall be the objectives?
- Objective 1: Effective use of Vaccines, Medicine tools and Technologies.
- Objective 2: Generating Innovations and Measuring it’s impacts.
- Objective 3: To sustain Commitment to drive Progress and harness the Multi-sectoral stakeholder engagement.
Phases of implementation
Mass vaccination of dogs and PEP in humans are strategies to curtail down the disease burden in our country.
Phase 1: Through training to Volunteers, Veterinary Professionals and Facilities for the Clinics for Surgical sterilisation, rabies vaccination, treatment of sick and injured dogs. Mobile units enabling the programme to be extended to rural regions.
Phase 2: Initiative under subsequent training activities would have a strong impact on animal welfare and have been critical for community acceptance of the programme and cost control. Multisectoral cooperation is essential for sustained rabies elimination. Implementing annual state wide rabies Vaccination, Free house to house vaccination, Penalty to the dog owners if their unvaccinated dog bites any other person, painting the vaccinated stray dogs for identification. Arranging Special Campaigns, Camps in the occasion of Zoonoses day and Rabies day annually among the general public.
Phase 3: Cooperation of villagers, panchayats , local bodies and Department of animal husbandry field officers is essential. Dog population management is important for programme goals of improved animal welfare and rabies control.
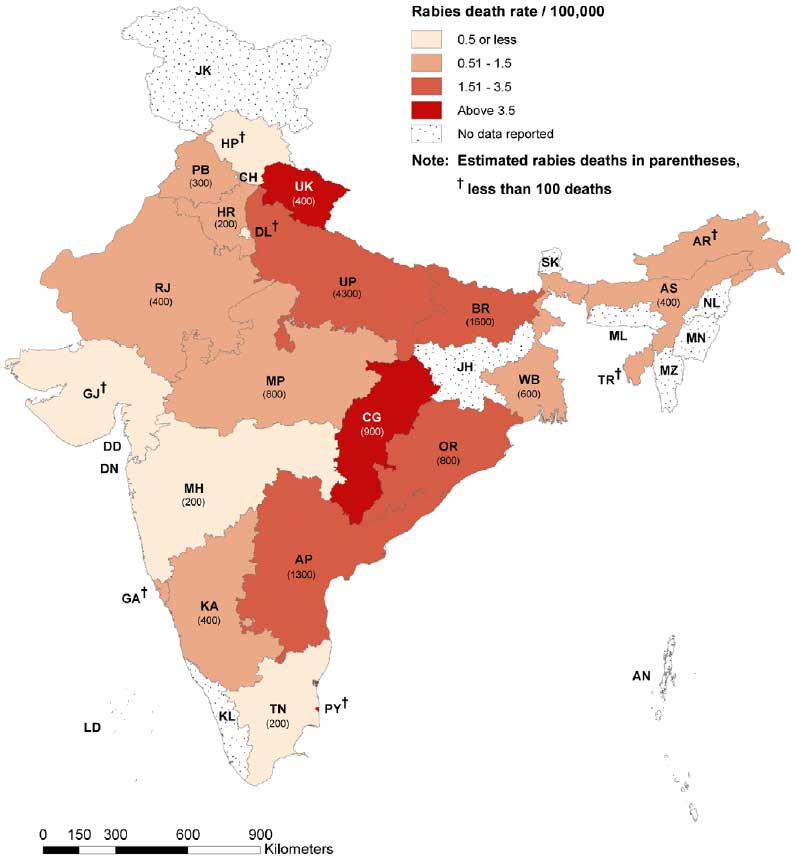
- Stages of this program can be implemented in a stepwise manner across the country. Beginning in the Endemic areas like Chhattisgarh, Uttar pradesh and Odisha then extended to moderately affected disease burden areas like Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Delhi, etc., then finally all throughout the nation.
- Building a strong foundation for rabies elimination by preparing the normative rules and structures to catalyse the action. Key activities include robust budget effective sustainable rabies elimination plans through One Health approach.
- Following the new strategies like IBCM – Integrated Bite Case Management (To determine whether the dog bite is likely to constitute exposure to rabies, will reduce the human treatment cost and prevents transmission risk) also reduce the cost and disease burden.
Conclusion
To make rabies elimination a reality by 2030, we need all sectors – Human, Animal and Environment Agencies cooperation through adopting One Health Approach. In the region of Asia, good progress in control of rabies has been shown by Thailand, Sri Lanka’s and the Philippines. If these countries have done it then, India must also do it. Finally, the freedom from dog mediated human rabies in India by 2030 must be viewed by the Government of India as a public health concern and India should occupy a place of pride in WHO by achieving this goal successfully. Time is short to reach these global targets, there is no cause for further delay. Rabies elimination is feasible the time to act is now.






Be the first to comment