“I’ve learned that making a ‘living’ is not the same thing as ‘making a life’”
The trout is a freshwater fish of Salmonidae family. Of the 15 trout species which are found worldwide, brown (Salmo Trutta Fario) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss (Old name Salmo Gairdneri)) are found in the country. The major trout producing states are Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Tamil Nadu and Kerala. It also tolerates low dissolved oxygen content of water and is resistant to some of the fish diseases. It is fast-growing indigenous fish in Indian waters. Of the two species of trout, brown has become domesticated in culture systems, streams and lakes, and has emerged as a self-sustaining population in the Himalayas. The rainbow trout, however, has remained confined to pond culture and is not very common in streams and rivers of India.

Schemes for promotion of trout farming in the state
Schemes of National Fisheries Development Board, Uttarakhand
|
S.No. |
Name of Project |
Details of Project |
|
1 |
Development of Reservoir (conservation and promotion of fisheries in natural water source) | Development of fisheries in natural water sources with help of local people |
|
2 |
Schedule Castes Sub Plan (SCSP) | Training for self-employment of SC persons
FOR SC : 70% subsidy (INR 49000) for plain areas on fishery pond of INR 70000/- per 0.20 hectare (unit). FOR SC : 70% subsidy (INR 42000) for hill areas on fishery pond of INR 60000/- per 0.01 hectare (unit). |
|
3 |
Tribe Sub Plan (TSP) | Training for self-employment of tribal persons
FOR Tribe : 70% subsidy (INR 49000) for plain areas on fishery pond of INR 70000/- per 0.20 hectare (unit). FOR Tribe : 70% subsidy (INR 42000) for hill areas on fishery pond of INR 60000/- per 0.01 hectare (unit). |
|
4 |
Adarsh Fishery Pond manufacture in hilly areas | Manufacture and making of Adarsh Fishery ponds in state
Manufacture of concrete pond of minimum 200 sq mtr/ 0.02 Hectare size (20x10x1.5 mtr/01 unit) area. 1st year subsidy INR 150000 (of total investment INR 300000). One candidate can have maximum 3 units. |
|
5 |
Fishery Pond manufacture in hilly areas | Small pond manufacture of 0.05-hectare area
Pond manufacture of 0.05 hectare/ 50-meter area with 50% subsidy of total cost i.e INR 25000/- of INR 50000/-. One candidate can have 3 units only. Training, field visit and holding public seminars for persons in fish cultivation |
|
6 |
Fish Cultivation Development Agency
(75% Center funded) |
Promotion of fish cultivation in plain area
Ponds manufacture and investment in fishery in plain areas of total cost INR 3,50,000 per hectare with 20% subsidy of INR 25000/- per hectare |
|
7 |
Development of cold water fishes (75% Center funded) | Promoting Fisheries in Hilly areas.
Constructing running water ponds in hilly areas and providing total investment of Rs. 60,000/- in which 20 percent is payable at 0.001 hectare (unit) i.e. Rs 12,000/Rs per 0.001 Hector |
|
8 |
National Fishermen Welfare Scheme (50% Center funded) | Social development of weak class fishermen.
Development of model villages for fishermen which includes: Rs. 75,000/- for the construction of home with drinking water system Rs 40,000 for one tube well (one in every 40 houses) – Insurance of fishermen |
|
9 |
Fisheries Training and Dissemination (80% Center funded) | Constructing fisheries training centers and running of training related programmes |
|
10 |
Database and information networking empowerment (100% Center funded) | Collecting data on various water resources development and related fishes and creating a state database of the information |
|
11 |
State fishery laboratory setting (75% Central Funded) | This includes – fishes health, diagnosis of diseases of fish and fish ponds, analyze the quality of water samples |
|
12 |
Integrated fisheries inland aquaculture and fisheries development (75 percent Central ) | Society / 1socail House Group through integrated fisheries in the state |
Promotion of Trout Farming: Unit cost Rs. 2.30 lakh Construction of trout raceway of size 15x2x1.5 m with investment cost of Rs. 1.00 lakh & subsidy @ 20% for General Category @ 25% for SC/ST on the approved unit construction cost. Provision of subsidy to farmers for first year inputs (feed & seed) totaling Rs. 1.30 lakh @ 20% of cost to General Category and @ 25% of cost to SC/ST.
Promotion of Trout Seed Hatchery Setting up of private seed hatchery with a capacity of 2-3 lakh fry / year with investment cost of Rs. 12.00 lakhs/unit. Subsidy is provided @ 20% of the unit cost for all farmers/ entrepreneurs.
Setting up of feed mill Feed mill with capacity of 1.2 Q per day with investment of Rs. 7.50 lakh and subsidy @ 20% of the investment cost up to a maximum of Rs. 1.50 lakh is available.
Schemes of State Govt. for Promotion of Trout Farming in Tribal Areas Unit cost Rs. 2.50 lakh Construction of trout raceway of size 15x2x1.5 m with a cost of Rs. 1.00 lakh. Subsidy @ 40% (Rs. 40,000/-) is provided for on the construction cost. Provision of subsidy to farmers for first year inputs (feed & seed) with a cost of Rs. 1.50 lakh @ 40% (Rs. 60,000/-) of cost.
Trout Fish Life Cycle
However, based on the field level feedback many of these farms are not fully functional due to various reasons such as siltation in tanks, high price of feed, temperature fluctuations, destruction of stock due to pesticide/ insecticide residues in water, theft etc. lack of insurance package for trout farming is also one of the major reasons which dissuades farmers from restarting his venture once a crop is destroyed.
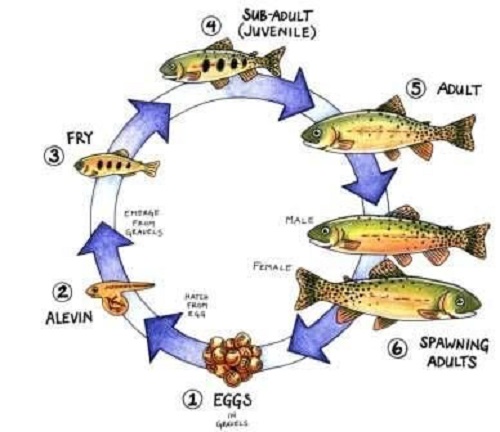
Trout will not spawn naturally in culture systems; thus, juveniles must be obtained either by artificial spawning in a hatchery or by collecting eggs from wild stocks. Larvae are well developed at hatching. In the wild, adult trout feed on aquatic and terrestrial insects, molluscs, crustaceans, fish eggs, minnows, and other small fishes, but the most important food is freshwater shrimp, containing the carotenoid pigments responsible for the orange-pink color in the flesh. In aquaculture, inclusion of synthetic pigments astaxanthin and canthaxanthin in aquafeeds causes this pink coloration (where desired).
Infrastructure Requirements of Trout Farm
Site Selection
Water is the most crucial deciding parameter for selection of site for setting up of trout farm. Site for commercial trout production must have a year-round supply of high quality water. The water to the farm can be from spring or from snow fed stream and must be free from silt.

Construction of ponds/ raceways the cemented ponds/ raceways are required for the culture of trout fish. The rectangular tanks are better than the circular cisterns. The economical size of a trout race way should be 12-15 m x 2-3 m x 1.2 – 0.5 m with an inlet and an outlet for overflow of water fixed with wire mesh screws to prevent the exit of stocked species. There should be a drain pipe at the bottom of the pond to facilitate the harvesting as well as the cleaning of tank from time to time.
Water supply in the farm
The water supply in trout farm should be through a filter bed/sedimentation tank. There is a problem of silt particularly during monsoon season when the water is turbid which is not good for trout farming. The quantity of water required for a trout farm is related with the stocking density, size of fish as well as the water temperature. Therefore, it is necessary to regulate the flow of water very carefully. For example, 30,000 fries need water flow of about 15 liters/minute, the fish below 250 g needs a water flow of 0.5 liters/kg/minute at 10-12°C.

The water flow of above-mentioned economical size of tank should be 52 m3 /hour for stocking of fingerlings of 5- 50 g at 15°C. Thus, the water flow is regulated in such a way that fishes should not assemble at one place and also do not move fast. Temperature and flow of water also plays important role in the production of trout. The pH of the water should be in the range of 7-8 with temperature in the range of 10-12°C.
Physico-chemical requirements of water for a trout farm:
The physico-chemical parameters for the successful culture of trout are temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH and turbidity.
Temperature: The fish thrives well within the temperature range of 5 to 18°C, but it has been found to tolerate the water temperature up to 25°C without any mortality. However, the maximum growth is obtained within the temperature range of 10 to 18°C.

Dissolved oxygen: The oxygen concentration range is from 5.8 to 9.5 mg/l. If the oxygen concentration is 5 mg/l, it is better to increase the flow of water.
pH: A neutral or slightly alkaline pH is best for the trout. The tolerable minimum and maximum pH values are 4.5 and 9.2, respectively. However, pH range of 7-8 is ideal for the growth of this fish.
Turbidity: The crystal-clear water is required and there should not be any contamination. The turbidity should not be more than 25 cm of Secchi disc transparency.
Stocking density: It is related with the water supply, water temperature, quality/water and types of feed. If water temperature is above 20oC, the stocking density should be less than the recommended density. The fry fingerlings (5 to 50 g) are stocked at the rate of 20 kg fish per cubic meter of water surface area.
Economics of trout farm
Investment cost
|
S.No. |
Particulars | Qty | Unit cost |
Total Cost (Rs.) |
|
1 |
Raceways – 15 x2 x 1.5 m | 1 | 100000 | 100000 |
|
2 |
Equipment (Dragnet, hand net, bucket, tubs, thermocool box etc.) |
LS |
6000 |
|
|
3 |
Capitalization of recurring expenditure | |||
| Seed | 4500 | 5 | 22500 | |
| Feed (Q) | 15 | 9700 | 145500 | |
| Interest cost for 1st Year | 26715 | |||
| Total | 3,00,715 | |||
Techno-economic parameters and assumptions:
| S.No. | Particulars | Unit/Amt |
|
1 |
Raceway size | 15x2x1.5 m |
|
2 |
No. of raceways | 1 |
|
3 |
Seed rate/ stocking density | 4500 nos. |
|
4 |
Mortality | 10% |
|
5 |
Seed cost (Rs. / piece) | 5 |
|
6 |
Feed consumption per raceway (Q) | 15 |
|
7 |
Feed cost (Rs. per Q) | 9700 |
|
8 |
Water flow rate in raceway (lps) | 10-15 |
|
9 |
Culture Period (year) | 1.5 |
|
10 |
Av. Wt. of fish at harvesting (kg) | 0.25 |
|
11 |
Sale price of fish (Rs. / kg) | 350 |
|
12 |
Miscellaneous cost / year (Rs.) | 6000 |
|
13 |
Labour (man-days) | 90 |
|
14 |
Labour Rate (per man-day) | 200 |
Feed: The quantity of feed mainly depends on the water temperature and size of fish. If the water temperature is above 18°C, the recommended feed should be reduced to just half of the required amount and above 20°C, better to stop the feeding. The feeding should also be suspended on a cloudy day and when the water is turbid.
| Ingredients | Percentage of ingredients | Quantity for preparing 10 kg of feed(kg) |
| Fish meal | 50 | 5 |
| Soya flakes | 10 | 1 |
| Groundnut cake | 20 | 2 |
| Wheat flour | 10 | 1 |
| Linseed oil | 9 | 0.9 |
| Supplevit-M | 1 | 0.1 |
| Choline chloride | 0.1 | 0.01 |
Feeding @ 4-6 % is necessary for the fingerlings for better growth but due consideration should also be given to the water temperature for following the feeding schedule. At the water temperature range of 10-12°C, feeding schedule of 6% is optimum but when it increases to 15°C, the feeding schedule to be lowered to 4% and beyond 19°C, it should be just 50% of the optimum schedule. The optimum growth rate per month is 80 g.

Production of Table size fish
The fish after gaining the weight of 250 g is advisable to be harvested because beyond this size the growth is slow and rearing is uneconomical. Trout processing wastes can be used for fish meal production or as fertilizer. The fresh fish market is large because the flesh is soft and delicate, white to pink in color with a mild flavor. Food market fish size can be reached in 9 months but ‘pan-sized’ fish, generally 280-400 g, are harvested after 12-18 months. Strict guidelines are in place for the regulation of rainbow trout for consumption with respect to food safety. Hygiene and safe transportation of fresh fish are of paramount importance, to ensure that fish are uncontaminated by bacteria, in accordance with food agency directives.

Hygiene
The cleanliness is a very important factor in trout farming. The trout should be cleaned and disinfected either with 10% formalin or 4 ppm KMNO4 solution periodically. The infected fish should be immediately removed from the tank and due care should be taken to consult some fishery expert regarding the disease, if any.
At present 30% handling/ Departmental charges are being levied on the feed. Department provides 15% subsidy on handling charges. There is a need to relook into the levy of handling charges and offer feed to farmers at no profit no loss basis. State Scheme for promotion of trout farming in tribal area which offers 40% subsidy need to be extended to NFDB scheme for trout farming which offers 20%/25% subsidy. Further, disparities in unit cost and subsidy among two schemes also need to be addressed. NFDB scheme for promotion of hatchery with capacity of 2-3 lakh fry by private entrepreneurs needs to be revised by lowering the capacity to 0.50-1.00 lakh since the capacity and capability of private entrepreneurs is limited. This would help the progressive farmers located at far off places to have captive production of trout seed. Training component on hatchery management also need to be included in the scheme.
Development or provision of floating feed instead of pellet feed will prevent feed loss during feeding and reduce production costs.






Be the first to comment